
And it will affect all of us.
This story was originally published by Grist and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
VW Pics/ZUMA Wire
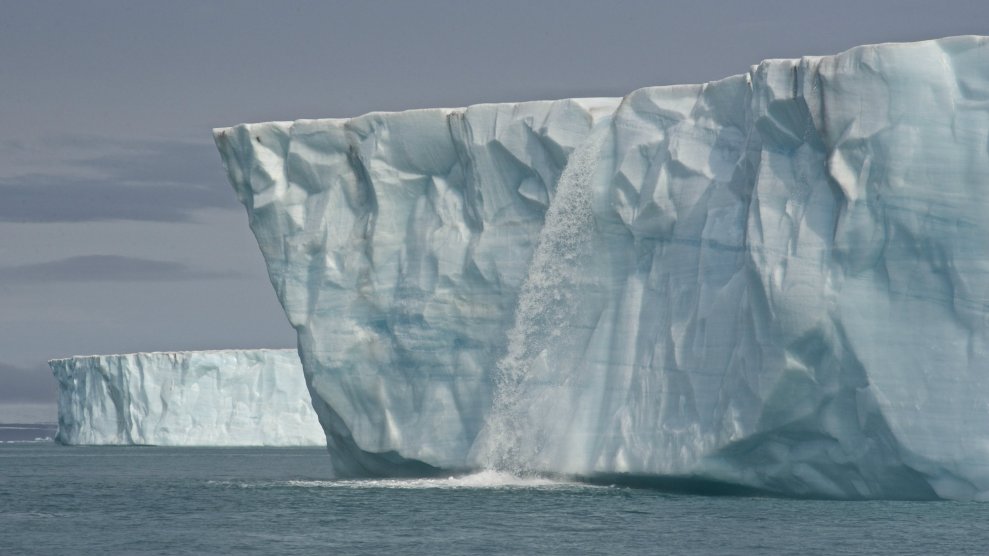
Last week, at a New Orleans conference center that once doubled as a storm shelter for thousands during Hurricane Katrina, a group of polar scientists made a startling declaration: The Arctic as we once knew it is no more.
The region is now definitively trending toward an ice-free state, the scientists said, with wide-ranging ramifications for ecosystems, national security, and the stability of the global climate system. It was a fitting venue for an eye-opening reminder that, on its current path, civilization is engaged in an existential gamble with the planet’s life-support system.
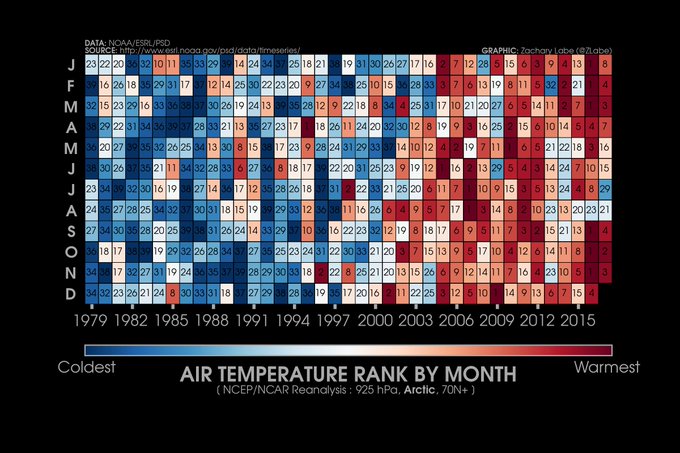
In an accompanying annual report on the Arctic’s health—titled “Arctic shows no sign of returning to reliably frozen region of recent past decades”—the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, which oversees all official U.S. research in the region, coined a term: “New Arctic.”
Until roughly a decade or so ago, the region was holding up relatively well, despite warming at roughly twice the rate of the planet as a whole. But in recent years, it’s undergone an abrupt change, which now defines it. The Arctic is our glimpse of an Earth in flux, transforming into something that’s radically different from today.
At a press conference announcing the new assessment, acting NOAA Administrator Timothy Gallaudet emphasizes the “huge impact” these changes were having on everything from tourism to fisheries to worldwide weather patterns.
“What happens in the Arctic doesn’t stay in the Arctic—it affects the rest of the planet,” Gallaudet said.
In an interview with NPR, marine scientist Jeremy Mathis, director of NOAA’s Arctic Program, went a step further. When it comes to the Arctic, Mathis said “there is no normal” anymore: “The environment is changing so quickly in such a short amount of time that we can’t quite get a handle on what this new state is going to look like.”
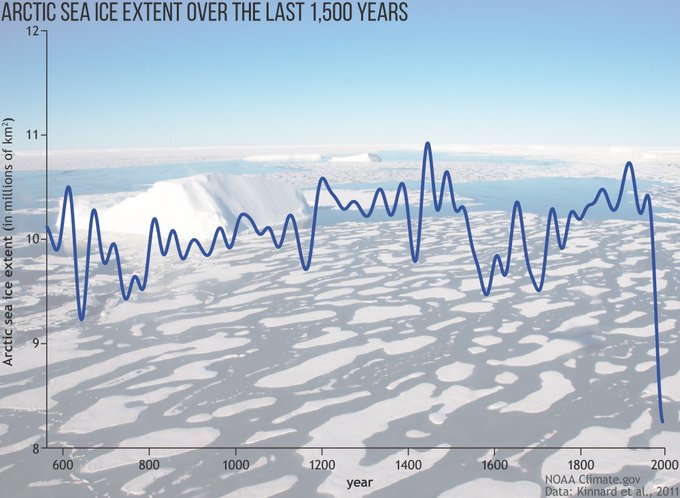
Using 1,500 years of natural records compiled from lake sediments, ice cores, and tree rings as context, the NOAA report says the Arctic is changing at a rate far beyond what’s occurred in the region for millennia.
“The rate of change is unprecedented in at least the last 1,500 years and probably going back even further than that,” Mathis said. “Not only are we seeing big changes, we’re seeing the pace of that change begin to increase.”
In the NOAA report, Arctic scientists lay out their best ideas of what this shift could mean for the world. Their depictions are sobering.
Take, for instance, the hypothesis of University of Alaska-Fairbanks permafrost scientist Vladimir Romanovsky: So far, 2017 has seen the highest permafrost temperatures in Alaska on record. If that warming continues at the current rate, widespread thawing could begin in as few as 10 years. The impact of such defrosting “will be very very severe,” Romanovsky says, and could include destruction of local infrastructure—like roads and buildings—throughout the Northern Hemisphere and the release of additional greenhouse gases that have been locked for generations in the ice.













Đăng nhận xét